Asthma: It's about inflammation
It's now understood that up to 84% of asthma patients have Type 2 airway inflammation, which is particularly associated with exacerbations.1
FeNO: Inflammatory biomarker
Type 2 inflammation is driven by T-helper 2 cells, which produce interleukins IL-4, IL-5 and IL-13. IL-4 and IL-13 upregulate nitric oxide levels in the lungs.2
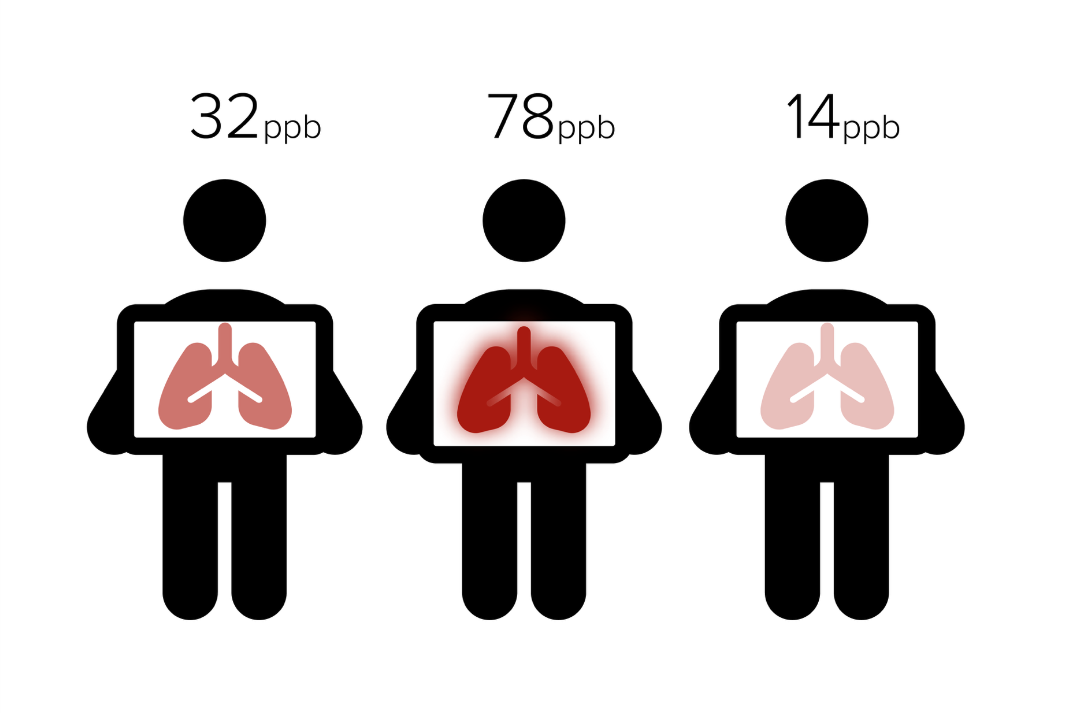
Your flare-up risk predictor
Elevated FeNO values are associated with 3.2x greater risk of exacerbations when compared to low FeNO levels.3
As knowledge of the underlying causes of asthma has evolved, diagnostic and management methods have too.
Biomarkers provide objective data on biologic parameters such as airway inflammation and disease activity. This can improve the understanding of asthma and lead to better patient outcomes.


Assess airway inflammation at the point of care


In 2011, the American Thoracic Society (ATS) produced a guideline recommending the cut-off points still used every day to interpret FeNO today.4 The cut-off points were derived from a large number of studies, where 83% of participants used NIOX® devices.5




Instantly transform your asthma care
Exacerbation risks can be increased by modifiable factors such as high airway inflammation, reduced lung function, poor adherence to ICS or inadequate inhaler technique.6
Understanding the level of inflammation with FeNO can lead to improved asthma care. FeNO levels are elevated in asthma and can provide healthcare professionals with the opportunity to see inside a patient’s lungs at the point-of-care.
"FeNO brings us one step closer to the precision medicine we all talk about"
Dr Priya Ilangovan (Paediatrician)
With half of asthma cases misdiagnosed, lung function testing is not enough to make a decision. Asthma diagnosis is up to 7x more likely with a high FeNO level.7
This is Dan
He is 8 and was recently sent to the emergency department after suffering severe shortness of breath during a footy match. A respiratory specialist suspected asthma but Dan's parents said he had no previous symptoms and doubted the diagnosis.
A quick FeNO test revealed that Dan's FeNO level was 58.ppb. This shows high Type 2 inflammation and an increased risk of exacerbation. Subsequent respiratory appointments with spirometry confirmed reversible airway inflammation.
FeNO testing supported the asthma diagnosis and helped Dan's parents to visualise the risk. They then agreed to ensure Dan takes his inhaled corticosteroid every day.


Therapy adherence is notoriously low in asthma with up to 43% of patients not taking their medication as prescribed.8 Those patients usually have higher FeNO levels, indicating a lack of control of airway inflammation due to missed doses of anti-inflammatory treatment.9
A high FeNO level indicates a greater risk of exacerbation.3 Using FeNO testing can uncover non-adherance and can be used as your asthma risk estimator to help reduce exacerbations by up to 50%.4
This is Victor
He has had asthma since the age of 3 and is prescribed an inhaled corticosteroid. Victor still experiences exacerbations and recently visited his doctor.
The doctor wanted to check whether Victor was using his inhaler properly and offered him a FeNO test. Victor had a FeNO level of 163ppb, indicating he is non-adherent to his medication and at risk of severe exacerbations. Seeing this number showed Victor how bad the situation actually was.
As part of his asthma management plan, Victor tested his FeNO regularly with the aim of reducing his FeNO to a normal level. Seeing his FeNO level reduce at every appointment motivated Victor to keep taking his medication. Victor’s FeNO is now 24ppb, his inflammation is under control and he has not had an asthma attack in the last year.
Severe asthma is usually defined as uncontrolled asthma despite adherence to maximal therapy and affects up to 10% of Australians with asthma.5 In the last few years, biologic treatments have been used as an effective means of improving asthma control and reducing exacerbations in severe asthma patients.
Most biologics target Type 2 inflammation pathways. FeNO testing is recommended by GINA, ERS and ATS to assess the Type 2 phenotype and predict a good response to certain biologics.5,10
This is Julia
Julia’s asthma had become increasingly difficult to manage, with frequent flare-ups despite regular use of inhaled corticosteroids (ICS). After a recent hospital visit, her doctor decided to investigate further to determine if she had severe asthma.
To help with the diagnosis, Julia's FeNO level was tested, revealing a high reading of 75 ppb. Based on this result, her doctor recommended biologic therapy to target her underlying inflammation and minimise further exacerbations. Over the next 12-months, Julia’s doctor watched her FeNO level decrease as she continued with her biologic treatment.
Julia’s asthma symptoms significantly improved. Her FeNO dropped to 24 ppb, and she was able to reduce her ICS dose while maintaining control over her asthma.

FeNO testing has been proven to considerably reduce costs and improve quality of life when used in asthma patients.
Are you eligible for reimbursement?
To be eligible, you must meet ALL of the following criteria:
About you:
- Respiratory laboratory
- Equipped to perform spirometry
- Performed with supervision from a specialist
- Performed with continuous attendance by a respiratory scientist
When measuring FeNO:
- Perform three FeNO measurements followed by three spirometry recordings (unless difficult to achieve for clinical reasons). Clinical reasons for not achieving three measurements must be documented
- Following FeNO, spirometry measurement must be performed before and after inhalation of a bronchodilator
- Retain a copy of the patient history stored within the NIOX device
Not applicable to a service associated with a service to which item 11503 or 11512 applies
Fee: $114.15 Benefit: 75% = $85.65 85% = $97.05
References
- Heaney LG et al. Eosinophilic and noneosinophilic asthma: an expert consensus framework to characterize phenotypes in a global real-life severe asthma cohort. Chest. 2021;160(3):814-830.
- Menzies-Gow A et al. Clinical utility of fractional exhaled nitric oxide in severe asthma management. Eur Respir J. 2020;55(3):1901633.
- Busse, W.W et al. Baseline FeNO as a prognostic biomarker for subsequent severe asthma exacerbations in patients with uncontrolled, moderate-to-severe asthma receiving placebo in the LIBERTY ASTHMA QUEST study: a post-hoc analysis. The Lancet Respir Med. 2021:9(10): pp.1165-1173.
- Dweik RA et al. An official ATS clinical practice guideline: interpretation of exhaled nitric oxide levels (FeNO) for clinical applications. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011;184(5):602-15.
- Data on file MKT-DOF-001. NIOX Group Plc.
- Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA). Global strategy for asthma management and prevention. 2021 update.
- Wang Z et al. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ). The clinical utility of fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO) in asthma management. Comparative Effectiveness Reviews, 197. 2017.
- Reddel H et al. Asthma control in Australia: a cross-sectional web-based survey in a nationally representative population. Medical Journal of Australia, 202: 492-496. https://doi.org/10.5694/mja14.01564
- McNicholl DM, et al. The utility of fractional exhaled nitric oxide suppression in the identification of nonadherence in difficult asthma. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 2012;186(11):1102-8.
- Holguin F, et al. Management of severe asthma: a European Respiratory Society/American Thoracic Society Guideline. European Respiratory Journal. 2020;55(1).